IRANDERMA |
|
Quiz: January 2004 |
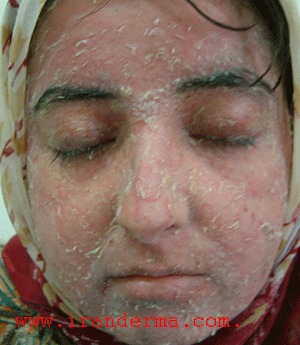
A 24-year-old female presented with several months history for erythematous, scaling and crusting lesions on her face, scalp and trunk. She had no oral lesion. The diagnosis is ?
Diagnosis: Pemphigus Foliaceous (PF)
PF can be divided into 4 subsets, all of which have identical immunopathologic features, but arise in unique circumstances. Idiopathic PF, Drug-induced PF, pemphigus erythematosus and Brazilian PF.
The cutaneous lesions of PF are similar in all subsets. lesions are almost always restricted to the cutaneous surface. Involvement of oral mucosa is extremely rare, and this is a major clinical differential point that distinguishes pemphigus vulgaris from PF.
The lesions often first arise in the central face, the head and neck, or the upper trunk and consist of very superficial crusts and erosion. The lesions may have a seborrheic appearance, but as they spread, more of a serous exudate forms. Lesions later extend from the upper cheat and back, head and neck to the extremity.
In pemphigus erythematosus there is often both clinical and laboratory evidence of coexistent lupus erythematosus.
Comment by; M. Mehravaran, MD
- Mehravaran M, Morvay M, Molnar K, Olah J, Korom I, Husz S, Dobozy
A: Juvenile Pemphigus Foliaceus. Br J Dermatol 139(3):469-499,
1998.
ايران درما |