IRANDERMA |
|
Quiz: March 2004 |
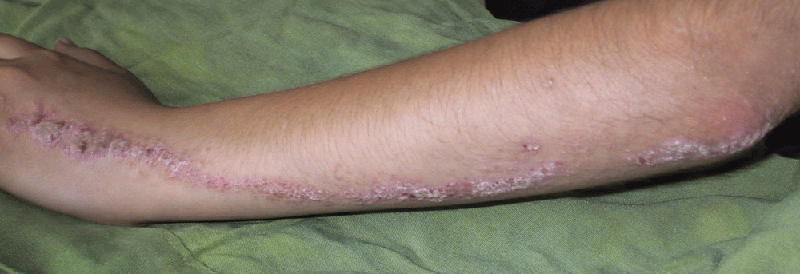
A 18-year-old male presented with a non-pruritic linear scaly lesion on his forearm since childhood. Histopathological examination revealed hyperkeratosis, acanthosis and papillomatosis. The diagnosis is ?
Diagnosis: Epidermal Nevus
Epidermal Nevi (EN) are hamartomatous lesions arising from the embryonic ectoderm. The case mentioned above is probably a case of “nevoid psoriasis” which usually considered being one of the variants of EN. Nevoid psoriasis is indistinguishable from ordinary psoriasis except in its distribution.
Linear epidermal nevi are present usually but not invariably at birth. They may be located anywhere and when located on only one side, often referred as “nevus unius lateralis”. Histologically LEN is similar to a benign papilloma and characterized by hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis and acanthosis.
Dermatitic or Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a distinctive type of epidermal nevus that differs clinically by the presence of itching and erythema and histologically by the presence of inflammation and columns of parakeratosis.
Lichen striatus usually appear suddenly. It is self limited and differs histologically by the presence of spongiosis and dyskeratosis.
Comment
by Dr. Mehrdad Mehavaran: Szeged/Hungary
The Linear epidermal Nevus is a verrucosus hyperplasia of epidermal cells. Nevus unicus lateralis is a term that has been used for linear unilateral lesions, and the term ichthyosis hysterix has been used for extensive bilateral lesions.
Clinically, theses have a verrucosus or irregular surface with color ranging from tan to dark brown with pattern of linear fashion. Any location is possible, although the extremities are perhaps most frequently involved.
Histologically, the changes in the epidermis are hyperplastic and affect chiefly the stratum corneum and stratum malpighii. There is variable hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis.
Differential Dg.
1. Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus (ILVEN): it differs clinically from other epidermal nevi by the inflammatory, often pruritic. Because of psoriasiform histologic appearance, differentiation from linear psoriasis has created some controversy, the clinical presentation, course, response to treatment, analysis of protein in the scale (Bernhard et al. Arch dermatol 1984;120;214-215) are not characteristic of psoriasis.
2. Lichen Striatus(LS): fairly common, self-limited, linear dermatosis of unknown origin that is seen primarily in the children, the early linear ILVEN is often the main source of confusion. The clinical course is usually more helpful than the morphologic features in distinguishing LS from epidermal nevi.
3. Other disorders to considers include linear lichen planus, linear porokeratosis, verruca plana, linear lichen nitidus, linear lichen simplex chronicus and linear Darier's disease.
ايران درما |