IRANDERMA |
|
Quiz: March 2010 |
|
What is your differentials for this 64-year-old woman with a 8- month history for these papular lesions? Her left lower eyelid is also involved. |
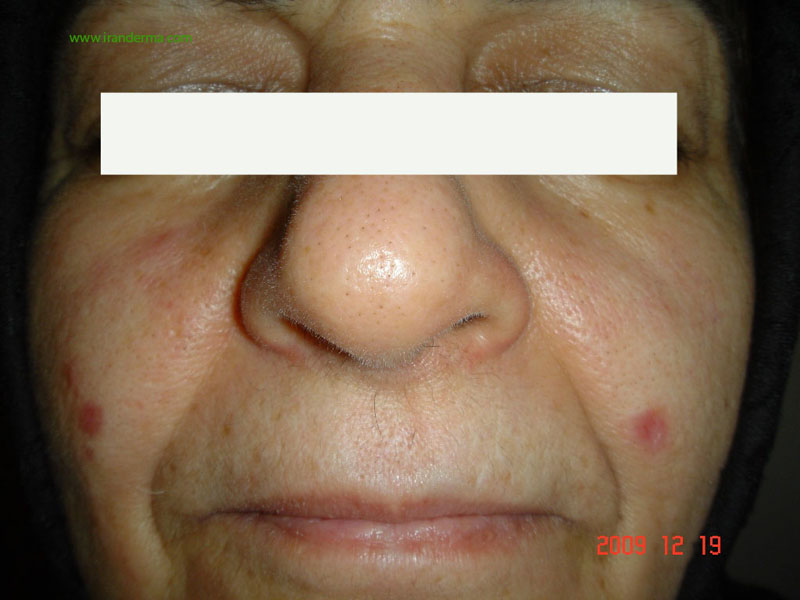
Diagnosis: Granuloma Faciale (GF)
Omid Zargari, MD, FAAD:
The first reported case of verified GF appears to be that of Wigley in 1945. GF is characterized by one to several soft, erythematous to livid papules, plaques or nodules, usually occurring on the face, although lesions may appear anywhere on the skin.
GF possesses clinical characteristics that are usually distinctive, but sometimes may be confused clinically with sarcoidosis, discoid lupus erythematosus, mycosis fungoides, benign lymphocytic infiltrate of Jessner, leprosy, erythema elevatum diutinum, polymorphous light eruption, lymphoma, fixed drug eruption, pigmented nevi, and granuloma annulare.
GF is notoriously resistant to therapy. Various treatment modalities have been used including dapsone, corticosteroids, antimalarials, isoniazid, clofazimine, topical nitrogen mustard and several surgical techniques have also been attempted, such as surgical excision, dermabrasion, cryotherapy and electrodessication.
ايران درما |